Table of Contents
Are fish considered reptiles?
This question has intrigued scientists and animal enthusiasts for years. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of fish and reptiles to uncover the truth behind their classification.
By exploring their evolutionary journey, defining characteristics, and genetic makeup, we will gain a deeper understanding of the relationship between these two groups of animals.
Key Takeaways:
- Fish and reptiles have distinct evolutionary paths and characteristics.
- The transitional fossil Tiktaalik Roseae provides crucial evidence of the shift from fish to land-dwelling animals.
- Understanding the vertebrate family tree helps us categorize different animal groups.
- Fish and reptiles possess unique physiological traits and adaptations for their respective habitats.
- The question of whether fish are reptiles is finally answered through scientific evidence and classification.
Exploring the Evolutionary Journey from Water to Land
The transition from water to land holds a significant place in the evolutionary history of animals. It marks a crucial moment when certain species adapted to survive and thrive on land, paving the way for the diverse terrestrial life we see today.
In this section, we will delve into the fascinating journey of evolution from water to land, exploring how ancestral connections between humans and fish provide insight into our shared evolutionary heritage.
Ancestral Connections between Humans and Fish
The path from fish to humans may seem distant and inconceivable at first glance. However, by examining the genetic and anatomical similarities between humans and fish, scientists have revealed surprising ancestral connections.
These connections offer glimpses into our evolutionary past and provide evidence of the remarkable unity of all life on Earth. Through these connections, we can trace our roots back to the earliest organisms that inhabited the aquatic world.
Insights from ‘Your Inner Fish’ Series
The groundbreaking series ‘Your Inner Fish’ takes us on a captivating journey through time, uncovering the ancestral remnants hidden within our own bodies. This television series, hosted by paleontologist Neil Shubin, shines a spotlight on the shared features and genetic blueprint that reveal our fishy origins.
By examining the adaptations and structures present in fish and how they have been modified over millions of years, we gain a deeper understanding of our evolutionary past.
Why Human Anatomy Owes a Lot to Fish
The human anatomy holds countless echoes of our fishy ancestors. From our limbs to our facial structure, fish have played a pivotal role in shaping the human form. The adaptations that allowed fish to navigate and thrive in water, such as gills, fins, and a flexible spine, have been repurposed and modified in humans for life on land.
Our ability to breathe using lungs, walk with limbs, and maintain balance owes a debt to the fish that ventured out of water before us.
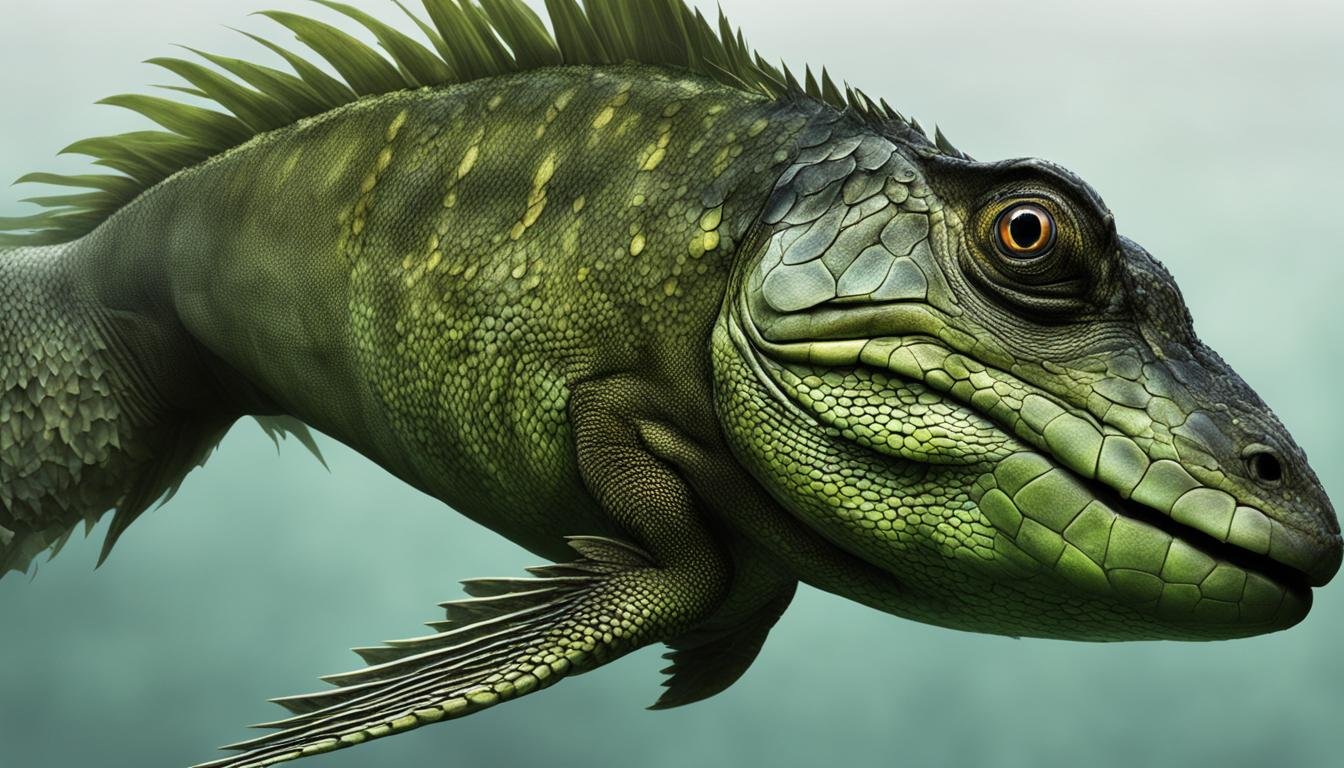
Meet Tiktaalik Roseae: The Fish with Limb-Like Fins
One of the most significant discoveries in the field of paleontology is Tiktaalik Roseae, a 375 million-year-old fish fossil. This fish, often referred to as the “fish with limb-like fins,” provides crucial evidence of the transition from fish to land-dwelling animals.
Tiktaalik Roseae possesses a unique combination of fish-like and tetrapod-like characteristics, making it a key player in understanding the evolutionary journey of vertebrates.

“The discovery of Tiktaalik Roseae is a game-changer in the realm of paleontology. It bridges the gap between fish and the first terrestrial vertebrates, offering invaluable insights into our evolutionary history,” says Dr. Jennifer Clack, an eminent paleontologist.
Tiktaalik Roseae, discovered in 2004 in Canada’s Arctic, had striking limb-like fins that resemble the limbs of early tetrapods, such as amphibians and reptiles. The fin structure, consisting of a wrist-like joint and a series of bones, allowed Tiktaalik to prop itself up and maneuver in shallow water or on land. These features made Tiktaalik well-adapted to the transitionary habitats between water and land during the Late Devonian period.
This ancient fish’s robust and specialized fins provided a glimpse into the evolutionary process that ultimately led to the development of limbs in land-dwelling organisms. By examining the structure and function of Tiktaalik’s fins, researchers have gained valuable insights into the momentous shift from aquatic to terrestrial life.
Deciphering the Vertebrate Family Tree
To truly understand the relationship between fish and reptiles, it is essential to decipher the vertebrate family tree. By exploring the backbone of evolution and categorizing vertebrates into fish, reptiles, amphibians, mammals, and birds, we can gain valuable insights into the similarities and differences between these groups.
Understanding the Backbone of Evolution
The vertebrate family tree represents the evolutionary history of animals with a backbone. It showcases the interconnectedness of different species and the common ancestry they share. By studying this family tree, scientists can unravel the mysteries of evolution and trace the origins of various vertebrate groups.
Categorizing Vertebrates: Fish, Reptiles, Amphibians, Mammals, and Birds
Within the vertebrate family tree, fish, reptiles, amphibians, mammals, and birds hold distinct places. Each group possesses unique characteristics and adaptations that contribute to their classification. Let’s take a closer look at these categories:
- Fish: Fish are aquatic vertebrates that typically have scales, fins, and gills. They encompass a wide range of species, including bony fish, cartilaginous fish (such as sharks and rays), and jawless fish (such as lampreys and hagfish).
- Reptiles: Reptiles are cold-blooded vertebrates that generally have dry, scaly skin and lay eggs. They include iconic animals like snakes, lizards, turtles, crocodiles, and alligators.
- Amphibians: Amphibians are cold-blooded vertebrates that typically have soft, moist skin, and undergo metamorphosis from aquatic larvae to terrestrial adults. They encompass frogs, toads, salamanders, and caecilians.
- Mammals: Mammals are warm-blooded vertebrates that have hair or fur, produce milk for their young, and give live birth. They include humans, as well as animals like dogs, cats, whales, bats, and elephants.
- Birds: Birds are warm-blooded vertebrates that have feathers, lay hard-shelled eggs, and possess beaks and wings. They encompass a diverse array of species, ranging from tiny hummingbirds to majestic eagles.
By categorizing vertebrates into these distinct groups, we can understand the evolutionary paths they have taken and appreciate the incredible diversity of life that exists on our planet.
Defining Characteristics of Fish Versus Reptiles
Fish and reptiles have distinct defining characteristics that set them apart from each other. In this section, we will delve into these characteristics, shedding light on the concept of cold-blooded ectotherms and the anatomical adaptations that enable fish to thrive in aquatic environments while reptiles adapt to both water and land.
A Closer Look at Cold-Blooded Ectotherms
Both fish and reptiles are considered cold-blooded ectotherms, meaning they rely on external sources of heat to regulate their body temperature. Unlike warm-blooded endotherms, such as mammals and birds, which can generate heat internally, fish and reptiles need the surrounding environment to maintain their body temperature. This adaptation allows them to conserve energy, as they don’t need to constantly produce heat like warm-blooded animals do.
Anatomy Adaptations for Aquatic and Terrestrial Lives
The anatomy of fish and reptiles reflects their different habitats and lifestyles. Fish possess streamlined bodies, with fins and gills that enable them to move and breathe efficiently in water. Their scales provide protection and reduce friction, allowing them to swim swiftly. In contrast, reptiles have evolved to adapt to both aquatic and terrestrial environments. They have lungs for breathing air, along with skin that helps prevent dehydration. Their limbs, whether adapted as fins or legs, enable them to navigate both land and water.

Clearing the Confusion: Are Fish Reptiles?
After exploring the evolutionary history, taxonomy, and characteristics of fish and reptiles, we can now address the burning question: Are fish reptiles? In this section, we will clear the confusion surrounding this topic and provide a definitive answer based on scientific evidence and classification.

When it comes to classifying animals, fish and reptiles fall into distinct categories based on their unique characteristics. Although both belong to the broader classification of vertebrates, they have key differences that set them apart.
Fish are aquatic animals with gills that extract oxygen from water, allowing them to breathe. They have streamlined bodies, scales, and fins, which enable them to move efficiently through water. Fish are typically cold-blooded, relying on their environment to regulate their body temperature.
On the other hand, reptiles are a diverse group of animals that inhabit various environments, including land, water, and air. They have lungs and breathe air, unlike fish. Reptiles are characterized by their scaly skin, which helps prevent water loss, and their ability to regulate body temperature through behavioral adaptations, such as basking in the sun or seeking shade.
Based on these defining characteristics, fish and reptiles are distinct groups of animals. While both share certain evolutionary connections as vertebrates, they have evolved separate traits and adaptations to suit their respective habitats.
In summary, fish and reptiles are not the same. Fish are specialized for aquatic environments, relying on gills and streamlined bodies to thrive underwater. Reptiles, on the other hand, have adapted to diverse environments and possess distinct features such as scales and lungs. Understanding the differences between these two groups enhances our appreciation for the incredible diversity of life on Earth.
The Tale of Scales and Skin: Analyzing Reptilian and Fish Features
The skin coverings of reptiles and fish are distinct and have evolved for different purposes. In this section, we will analyze the scale patterns and skin textures of reptiles and fish, exploring their evolutionary purpose. By understanding these features, we can gain further insights into the classification and adaptations of these animals.
Scale Patterns and Skin Textures
Reptiles and fish exhibit a wide variety of scale patterns and skin textures that contribute to their unique characteristics. Reptiles typically have scales that are larger, thicker, and more rigid, providing them with protection against predators and harsh environmental conditions.
On the other hand, fish scales tend to be smaller, thinner, and more flexible, allowing for streamlined movement through water and efficient oxygen exchange. The scale patterns of fish can vary greatly, from the small overlapping scales seen in species like trout to the larger, diamond-shaped scales found in carp.
Evolutionary Purpose of Reptilian and Fish Coverings
The evolutionary purpose of reptilian and fish coverings lies in their ability to adapt to their respective environments and fulfill specific functions.
Reptilian scales, with their robust and protective nature, aid in reducing water loss and preventing injury. They also play a crucial role in thermoregulation, allowing reptiles to regulate their body temperature by absorbing and radiating heat. Furthermore, the distinct scale patterns found in reptiles, such as the diamond-shaped scales in snakes, provide camouflage and aid in predator avoidance.
Fish scales, with their smaller size and flexibility, promote streamlined movement through water, reducing drag and increasing swimming efficiency. They also serve as a protective layer against parasites and pathogens that can harm fish in their aquatic habitats. Moreover, the diverse scale patterns in fish can provide camouflage, helping fish blend into their surroundings and avoid predation.
| Reptilian Features | Fish Features |
|---|---|
| Large, rigid scales | Small, flexible scales |
| Thermoregulation | Streamlined movement through water |
| Protection against predators | Protection against parasites and pathogens |
| Camouflage and predator avoidance | Camouflage and predator avoidance |
Understanding the distinct scale patterns and skin textures of reptiles and fish provides valuable insights into their evolutionary adaptations and survival strategies. These features not only contribute to their physical attributes but also play a crucial role in their interactions with the surrounding environment and other organisms.
Respiratory Revelations: How Fish and Reptiles Breathe
The respiratory systems of fish and reptiles play a crucial role in supporting their unique lifestyles. Let’s explore the fascinating ways in which these animals breathe and adapt to their environments.
When it comes to fish, their respiratory system allows them to efficiently extract oxygen from water. Instead of lungs, fish have specialized organs called gills. These gills are located on the sides of their body and contain thin filaments that are rich in blood vessels. As water flows over the gills, oxygen is extracted and carbon dioxide is released, allowing fish to respire underwater.

On the other hand, reptiles have a more diverse respiratory system that enables them to breathe in both aquatic and terrestrial environments. Most reptiles have lungs similar to mammals, which allow them to respire air. However, some reptiles, like turtles and tortoises, possess specialized structures in their bodies such as a bony shell or a chambered lung, which help them adapt to different lifestyles.
The respiratory adaptations of fish and reptiles shed light on their unique classification and survival strategies. By understanding how they breathe and obtain oxygen, we gain insights into their ability to thrive in their respective habitats.
Diving into the Genetics of Early Vertebrates
The genetic makeup of early vertebrates holds valuable clues about the evolutionary relationships between fish and reptiles. By studying their genetic code, we can gain a deeper understanding of their evolutionary history and explore their shared genetic characteristics as well as the factors that differentiate them from each other.
To illustrate this, let’s take a closer look at the genetic makeup of fish and reptiles:
“The genetic analysis of early vertebrates has provided significant insights into their evolutionary relationships. Scientists have discovered that fish and reptiles share many genetic similarities, particularly in their early embryonic development. However, there are also specific genetic differences that have contributed to the divergence of these two groups.”
To further explore the genetics of these animals, we can visualize the following table:
| Genetic Characteristics | Fish | Reptiles |
|---|---|---|
| Scale Formation | Genes involved in scale formation contribute to their unique skin coverings. | Similar genes as fish, but modified for different scales and skin types. |
| Egg Development | Distinct genetic mechanisms regulate egg development and fertilization. | Similar genetic processes in reptiles but with adaptations for amniotic egg formation. |
| Metabolic Regulations | Genes involved in metabolic processes adapt to aquatic environments. | Metabolic genes enable adaptations for both aquatic and terrestrial environments. |
| Microevolutionary Changes | Species-specific genetic variations influence external appearance, behavior, and physiological traits. | Genetic changes lead to adaptations for different ecological niches and reproductive strategies. |
As seen in the table above, fish and reptiles share common genetic characteristics, such as scale formation and metabolic regulations. However, they have unique genetic adaptations that allow them to survive in their respective habitats. These genetic differences have played a crucial role in shaping the evolutionary paths of fish and reptiles.
Ever-changing Ecosystems: Fish and Reptiles’ Survival Strategies
Fish and reptiles have developed unique survival strategies to thrive in ever-changing ecosystems. These adaptations allow them to navigate and conquer various environments, from the depths of the ocean to the deserts and forests of the land.
Adaptations to Aquatic and Dry Environments
In aquatic environments, fish have evolved remarkable adaptations that enable them to survive and thrive. Their streamlined bodies, paired with fins and tails, facilitate efficient movement through water. Gills allow them to extract oxygen from the water, while specialized swim bladders provide buoyancy control.
Reptiles, on the other hand, have adapted to both aquatic and dry environments. Some reptiles, like turtles and crocodiles, are adept at navigating through diverse aquatic habitats. Their streamlined bodies, powerful limbs, and scaly skin contribute to their success in water.
When it comes to surviving in dry environments, reptiles have developed numerous strategies. Many reptiles, such as snakes and lizards, possess scales that aid in water retention and protection against water loss. Some reptiles, like certain species of lizards and tortoises, have the ability to extract moisture from their food, reducing their reliance on external water sources. Additionally, behavioral adaptations, such as basking in the sun to regulate body temperature, play a crucial role in their survival.
Both fish and reptiles have mastered the art of adapting to their surroundings, allowing them to inhabit a wide range of habitats and exploit available resources.
Evolving from Fins to Limbs: How Creatures Adapted to Land
The transition from aquatic to terrestrial life required significant adaptations. Fish evolved into tetrapods, creatures with limbs, enabling them to move and support their body weight on land. This transition, often referred to as the ‘fins to limbs’ evolution, marked a crucial milestone in the history of life on Earth.
The Tiktaalik roseae, a remarkable fossil discovery, provides crucial evidence of this evolutionary transition. With its limb-like fins, Tiktaalik represents an intermediate stage between fish and land-dwelling animals. This fossil sheds light on the anatomical changes that occurred during the fins-to-limbs evolution, such as the development of a wrist-like structure and a robust ribcage.
As amphibians emerged from the water, reptiles followed suit, becoming the first truly terrestrial vertebrates. Reptiles evolved adaptations that allowed them to overcome the challenges of life on land. These include waterproof scales, efficient kidneys for conserving water, and shelled eggs with self-contained embryonic environments.
Overall, the transition from fins to limbs was a monumental evolutionary feat. It opened up new possibilities for vertebrates, paving the way for diverse terrestrial life forms we see today.

Essential Care for Aquatic and Reptilian Pets
If you’re considering keeping fish or reptiles as pets, it’s essential to understand their unique care requirements. In this section, we will discuss the essential care needed for aquatic and reptilian pets, including their specific habitat requirements and tips for maintaining a healthy environment. By following these guidelines, you can ensure the well-being of your beloved pets.
Unique Habitat Requirements for Fish and Reptiles
Fish and reptiles have distinct habitat requirements that must be met to ensure their health and happiness. Let’s take a closer look at the specific needs of these aquatic and reptilian pets:
- Care for Aquatic Pets:
- Aquarium Size: Choose an aquarium that provides ample space for your fish to swim and explore. Research the specific requirements of your fish species and consider factors such as the number of fish, their size, and their territorial behavior.
- Water Quality: Regularly monitor and maintain the water quality in the aquarium. This includes maintaining appropriate temperature, pH levels, and filtration systems. Perform regular water changes to keep a clean and healthy environment for your fish.
- Decorations and Plants: Add suitable decorations and live plants to the aquarium to provide hiding spots and create a more natural habitat for your fish. Ensure that any decorations or plants are safe for your fish and won’t harm them.
- Nutrition: Feed your fish a balanced diet that meets their specific nutritional needs. Research the dietary requirements of your fish species and provide a variety of high-quality fish food to promote their overall health and vitality.
- Care for Reptilian Pets:
- Enclosure Setup: Create an appropriate enclosure that resembles the reptile’s natural habitat. Consider factors such as temperature gradients, lighting, substrate, and hiding spots. Different reptiles have different enclosure requirements, so research your specific reptile species to ensure you meet their needs.
- Temperature and Humidity: Monitor and maintain the proper temperature and humidity levels in the enclosure based on the requirements of your reptile. Use heating devices, UVB lighting, and misting systems to create a suitable environment that mimics their natural habitat.
- Nutrition: Provide a balanced diet that meets the specific nutritional needs of your reptile. Different reptiles have different dietary requirements, so research your reptile species to determine the appropriate food items and feeding schedule.
- Cleaning and Hygiene: Regularly clean and disinfect the enclosure to prevent the build-up of bacteria and parasites. Remove waste, replace substrate if necessary, and ensure that the environment remains clean and odor-free.
Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Environment for Your Pets
Creating a healthy environment for your aquatic and reptilian pets goes beyond meeting their specific habitat requirements. Here are some additional tips to ensure the well-being of your pets:
- Regular Monitoring: Regularly monitor the temperature, humidity, and water quality in the enclosure or aquarium. This will help you identify any potential issues or changes that may affect your pets.
- Provide Enrichment: Enrich your pets’ environment by offering them opportunities for mental and physical stimulation. This can include providing toys, hiding spots, and interactive feeding methods. Enrichment activities help prevent boredom and promote their overall well-being.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Schedule regular vet visits to ensure your pets are in good health. A veterinarian specializing in aquatic or reptilian care can provide you with valuable advice and identify any potential health issues early on.
- Research and Education: Continuously educate yourself about the specific care requirements of your aquatic or reptilian pets. Stay up to date with the latest research, best practices, and advancements in caring for these unique animals.
By providing the necessary care and maintaining a healthy environment for your aquatic and reptilian pets, you can enjoy the companionship of these fascinating creatures and ensure their well-being for years to come.
Conclusion
In conclusion, after thoroughly exploring the evolutionary journey, classification, anatomy, and genetics of fish and reptiles, we have gained a deeper understanding of their interconnections. While fish and reptiles have distinct characteristics, they also share a common evolutionary heritage that is worth revisiting and appreciating.
By recognizing our shared evolutionary heritage, we can develop a greater appreciation for the diversity of life on Earth. The intricate wonders of the natural world are a testament to the remarkable adaptations and survival strategies developed by fish, reptiles, and other species throughout history.
Embracing the diversity of life on Earth is not only intellectually stimulating but also crucial for our collective responsibility in preserving our planet’s delicate ecosystems. As we strive to protect and conserve our natural environments, let us remember the rich history and interconnectedness of all living organisms, allowing us to live harmoniously with our fellow creatures.
FAQ
Are fish considered reptiles?
No, fish are not considered reptiles. While they both belong to the larger group of vertebrates, fish and reptiles are distinct classifications with different characteristics and evolutionary histories.
What are the defining characteristics of fish and reptiles?
Fish and reptiles possess distinct characteristics that differentiate them from each other. Fish are cold-blooded ectotherms with adaptations for thriving in aquatic environments, while reptiles can adapt to both water and land and have unique physiological traits.
How do fish and reptiles breathe?
Fish have specialized gills that allow them to extract oxygen from water, while reptiles have lungs and can breathe in both aquatic and terrestrial environments.
What is the genetic makeup of fish and reptiles?
Fish and reptiles share some genetic characteristics as vertebrates, but they also have factors that differentiate them from each other. Studying their genetic code provides insights into their evolutionary history and relationships.
What are the habitat requirements for keeping fish and reptiles as pets?
Fish require specific aquatic habitats with appropriate water temperature, filtration, and tank size. Reptiles, on the other hand, need habitats that mimic their natural environment, with proper lighting, heating, and substrate.
